If you are suffering from chronic or recurrent headaches, you should consult your doctor and they may conduct physical and neurological exams to pinpoint the type and cause of your headaches using these approaches.
For this you need to undergo certain diagnosis and in this your doctor will help you to understand about the headache and a description of your pain.
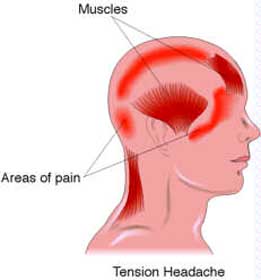
- Pain characteristics. Does your pain pulsate? Or is it constant and dull? Sharp or stabbing?
- Pain intensity. A good indicator of the severity of your headache is how much you're able to function while you have it. Are you able to work? Do your headaches wake you or prevent you from sleeping?
- Pain location. Do you feel pain all over your head, on only one side of your head, or just on your forehead or behind your eyes?
Imaging tests
If you are suffering from some serious, unusual and complicated headaches, then your doctor may order some tests to rule out serious causes of pain such as tumor and other issues. Two common tests used to image your brain include:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). An MRI scan combines a magnetic field, radio waves and computer technology to produce clear images.
- Computerized tomography (CT). A CT scan is a diagnostic imaging procedure that uses a series of computer-directed X-rays to provide a comprehensive view of your brain.
Treatment
Generally human beings suffering from headaches don’t take it seriously and don’t seek any medical attention and try some natural or home remedies to get rid of it. Intake of over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers can result hazardous for health in the later age
Acute medications
Both OTC and prescribed medicines are available to reduce the pain of a headache which is included in the variety of medications.
Pain relievers. the first line of treatment for reducing headache pain are simple OTC pain relievers are usually. These include the drugs aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen (Aleve).
Prescription medications include naproxen (Naprosyn), indomethacin (Indocin) and ketorolac (Ketorolac Tromethamine).
- Combination medications. Aspirin or acetaminophen or both are often combined with caffeine or a sedative drug in a single medication. Combination drugs may be more effective than are single-ingredient pain relievers. Many combination drugs are available OTC.
- Triptans and narcotics. For people who experience both migraines and episodic tension headaches, a triptan can effectively relieve the pain of both headaches. Opiates, or narcotics, are rarely used because of their side effects and potential for dependency.
Preventive medications
if you have frequent or chronic headaches that aren't relieved by pain medication and other therapies then your doctor may prescribe medications to reduce the frequency and severity of attacks, especially if you have frequent or chronic headaches that aren't relieved by pain medication and other therapies.
Following are included:
- Tricyclic antidepressants. Tricyclic antidepressants, including amitriptyline and protriptyline, are the most commonly used medications to prevent tension headaches. Side effects of these medications may include constipation, drowsiness and dry mouth.
- Other antidepressants. There also is some evidence to support the use of the antidepressants venlafaxine (Effexor XR) and mirtazapine (Remeron).
- Anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants. Other medications that may prevent tension headaches include anticonvulsants, such as topiramate (Topamax). More study is needed.
Don't get frustrated if you haven't seen improvements shortly after you begin taking the drug because preventive medications may require several weeks or more to build up in your system before they take effect
Monitoring of your treatment will be done by your doctor to see how the preventive medication is working. Do not have overuse of pain relievers for your headaches cause this can lead to other health related problems in the long run. Instead book a specialist at Quickobook.com now, and get your confusions cleared out!








Comments (0)
No comments yet. Be the first to share your thoughts!
Leave a Comment